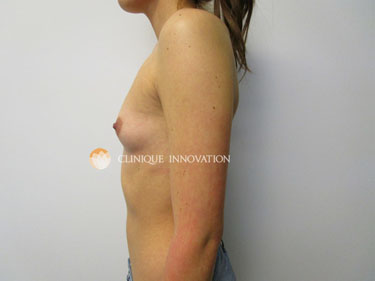
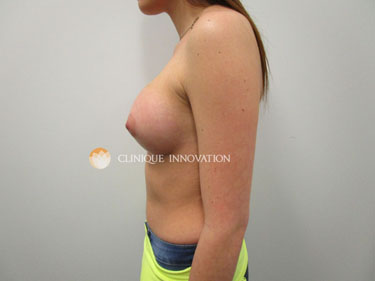
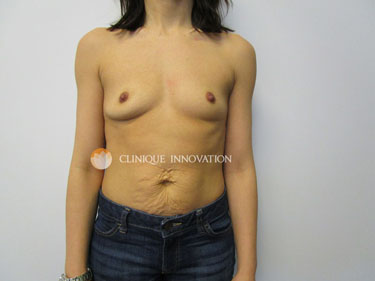
A breast augmentation is a surgical procedure in which an implant is placed behind the breast tissue to increase breast volume and create a balanced silhouette, whether you have relatively small breasts, would like to replace the volume you lost in your breasts over the years, or following a pregnancy or significant weight loss.
For some women, a breast augmentation helps improve their body image and even boosts their self-esteem and confidence. In general, women looking into a breast augmentation feel that their breasts are too small in comparison with their body proportions or that their breast volume has decreased following a pregnancy. Other women naturally have one breast which is sensibly smaller than the other and would like to correct the visible asymmetry. Finally, breast reconstruction using implants helps achieve a natural appearance in cancer patients following a mastectomy.
“Our goal is to create a beautiful natural appearance.”
In short, women who are interested in a breast augmentation simply hope to achieve a balanced silhouette and perfect the proportions of their natural curves.
Contrary to the negative image which is often presented by the press, most clients who are interested in a breast augmentation would rather avoid the dramatic “fake breasts” look. Our goal is to create an appealing natural appearance which will often be mistaken as your natural assets!

What are the different types of implants?
The implants sold in Canada contain either silicone gel or saline in a silicone shell (i.e., a natural inert component frequently used in various medical implants).
Silicone gel implants
This type of implant gives a natural appearance and their texture is closer to that of breast tissue. They are less likely to cause visible rippling, i.e., when you can see the folds in the implant through thin skin. Consequently, silicone gel implants are more often favoured for the final step of breast reconstruction in cancer patients.
Saline implants (salt water)
This type of implant is an excellent option for women who want to avoid silicone gel implants or who have unique requirements. Rippling is more visible with saline implants. Furthermore, this type of implant is more palpable, i.e., easier to feel.
Frequently asked questions
The breast augmentation procedure in itself lasts approximately an hour and a half, but the surgery may be longer if combined with other procedures.
However, you must plan some time for preparation before entering the operating room (30 to 45 minutes) and time to recover from the general anesthesia (1 to 3 hours). You should therefore plan to take a day off from work for your surgery.
We are responsible for educating our patients about their surgical options and the risks involved. We also encourage them to consider proven scientific facts regarding breast implants before looking into surgery. Many patients are interested in the safety of silicone implants and surgeons are frequently asked about it.
Note that all implants used are safe, whether they are filled with silicone gel or saline. Furthermore, the outer shell of all implants is silicone-based.
The use of silicone in medical implants is not a recent innovation. Quite the contrary, medical silicone has been used in different forms for decades (e.g., in intravenous lines, tubes in children’s ears, pacemakers, etc.) Numerous clinical and epidemiological studies conducted over a period of ten to thirty years have proven the safety of silicone gel implants and failed to establish a link between implants and the development of cancer.
1) Infection
Breast implants are unlikely to get infected. In order to prevent post-operative infections, you will receive antibiotics for five days beginning the day before the surgery.
2) Capscular contracture
Capsular contracture is a tightening of the scar tissue around an implant which may occur in certain patients. Normally, our bodies react to the presence of a foreign body by forming a pocket of scar tissue around it. Ideally, the cavity is large enough to allow for tiny movements resulting from the body changing positions, as with natural breasts. In the case of excessive scarring, the pocket could contract, becoming too tight and preventing the implant from moving. This results in the breast becoming firmer. Its shape may change and, in extreme cases, it may become painful.
An infection or hematoma (accumulation of blood around the implant) increases tissue inflammation around the implant, stimulating the scarring process which is a risk factor associated with the development of capsular contracture.
These risk factors must be decreased in order to prevent capsular contracture. To do so, your surgeon will use antibiotics and provide you with detailed information on how to massage breast implants. He will follow up with you after your operation to make sure you are healing well and to check on the outcome of the surgery. An additional surgery may be recommended in exceptional cases, such as if the patient develops painful capsular contracture (which is extremely rare).
3) Ruptured implant
A breast implant cannot be guaranteed for your entire life. Although a ruptured implant may sound like a big deal, it is not a medical emergency and does not represent a risk to your health.
When a saline implant deflates, your body absorbs the sterile fluid which drains from it. As a result of this benign process, the breast’s volume gradually decreases. A deflated saline implant can be removed or replaced by a new saline or silicone gel implant at any time, at your discretion.
Contrary to the saline solution, which is absorbed by the body, silicone is inert and waterproof. When a silicone gel implant ruptures, the gel pours out into the pocket in the breast. This could occur as a result of a major trauma to the breast, such as a high-speed car accident or a stabbing to the thorax. An ultrasound or MRI can be used to assess the integrity of the implant’s shell and to detect any silicone gel which may be leaking out of it. If a silicone implant breaks, it is recommended that it be removed or replaced, but it is not necessarily a medical emergency and the implant’s removal or replacement can be planned at your discretion.
You must avoid any intense physical exercise, raising your arms above your shoulders and lifting weights heavier than 5 pounds during the first two to three weeks following your surgery in order to give your body a chance to heal comfortably. You can resume your normal physical activities four to six weeks after your surgery. It is important for you to listen to your body. It will tell you if you are ready to exercise and how much exercise you can handle. Pain or discomfort when exercising is a sign that your body is not quite healed and that it would be better to wait a few weeks before trying again.
The incision made for a breast augmentation creates a fine linear scar which is hidden in the crease beneath the breast. If a breast lift is performed at the same time as the augmentation, additional incisions will be necessary, but they will not be visible when wearing a bra or bikini top.
he ideal patient for this procedure is in good general health, physically fit and at her ideal body weight (or has reached a stable weight after significant weight loss). She may have relatively small breasts in comparison with her body size or she may simply be interested in increasing her breast size.
Women who elect breast augmentation surgery are often aiming to achieve a padded or push-up bra effect. Mothers may be interested in regaining the appearance they had while breastfeeding or before their pregnancies.
Breast augmentation surgery is sometimes combined with a breast lift (mastopexy) in the presence of significant sagging. Based on a physical examination, your plastic surgeon can assess whether a combination of these two techniques would be appropriate for you.
As long as the tissue and ducts of the breast are not divided during surgery, all of the structures leading to the nipple (including lactiferous ducts, sensory nerve fibres and vital blood vessels) will remain intact.
Your ability to breastfeed should not be altered in any way following a breast augmentation, assuming that you were fully able to breastfeed following pregnancy prior to the surgery.
The sensory nerve fibres leading to the nipple are not divided during a breast augmentation. Therefore, nipple sensitivity should remain unchanged following the procedure.
Regardless of your implant’s location (under the pectoral muscle or not), content (silicone gel or saline solution) and size, a breast augmentation will not interfere with the results of a self-exam, a physical examination by a doctor, an ultrasound, an MRI or any other method of screening for cancer.
A breast augmentation will not change your personal risk of breast cancer and breast implants do not impede cancer screening. If you are over the age of 50, a basic preoperative mammogram is recommended before any breast surgery. If you are under 50 years of age, preoperative screening is only recommended if a member of your immediate family has a history of breast or ovarian cancer. During the consultation, your surgeon will request information regarding your medical history and refer you to specialists or for screening tests as needed.
When getting a mammogram, advise the technician so that additional images may be captured (from a different angle) in order to get a clear view of all the breast tissue surrounding the implants.
Over the course of your life, you will probably need at least one additional surgery for your implants, be it to remove or replace them, or to adjust their volume according to your needs and personal preferences. Note that it is not necessary to change your implants regularly.
Your surgeon will follow up with you over the long term to make sure that you look and feel as good in the years following your surgery. There is no reason to undergo any further surgeries unless there is a problem or you would like to have an additional surgery.
The final cost of your treatments will be calculated on an individual basis in accordance with your needs. The cost of a breast augmentation generally varies between $8,130 and $11,530. When combined with a breast lift, the operation can cost between $13,075 and $18,945. Additional charges may apply if the patient has a particular condition, or if different surgeries are combined.
Our specialists

Plastic and aesthetic surgeon
Dr. Mario Luc
- 450-241-6045

PLASTIC AND AESTHETIC SURGEON
Dr. Marie-Pascale Tremblay-Champagne
- 450-241-6045

PLASTIC AND AESTHETIC SURGEON
Dr. Camille Vallée-Gravel
- 450-241-6045

PLASTIC AND AESTHETIC SURGEON
Dr. Jennifer Dolmajian
- 450-241-6045
Cosmetic surgeries
Make an appointment with a surgeon
Call Us
We would be glad to help you through the process by answering all your questions and allaying your concerns.